DNV GL announced the completion of the LNGreen joint industry project, which worked to develop a state-of-the-art next-generation LNG carrier. The LNGreen joint industry project brought together experts from DNV GL and industry specialists from GTT, Hyundai Heavy Industries, and shipowner GasLog. The vessel concept has a significantly improved environmental footprint, a higher level of energy efficiency, as well as an improved boil-off rate and cargo capacity, making it much better suited to future trading patterns than existing vessels.
LNGreen investigated the improvement of efficiency and performance of LNG carriers by considering actual operational conditions and optimisation in terms of hydrodynamics, machinery and system configuration. These developments were based on DNV GL’s integrated systems engineering approach COSSMOS, computational fluid dynamics calculations (CFD), and a containment system design. Martin Davies, the Project Manager at DNV GL stated that “using enabling computer tools we managed to develop a vessel which is approximately 8% more energy efficient and has increased its cargo volume capacity by 5%. The design is future compliant with new IGC code, Panama requirements as well as significant advances in a range of features, including the speed-range flexibility, hull form and boil-off rate”.
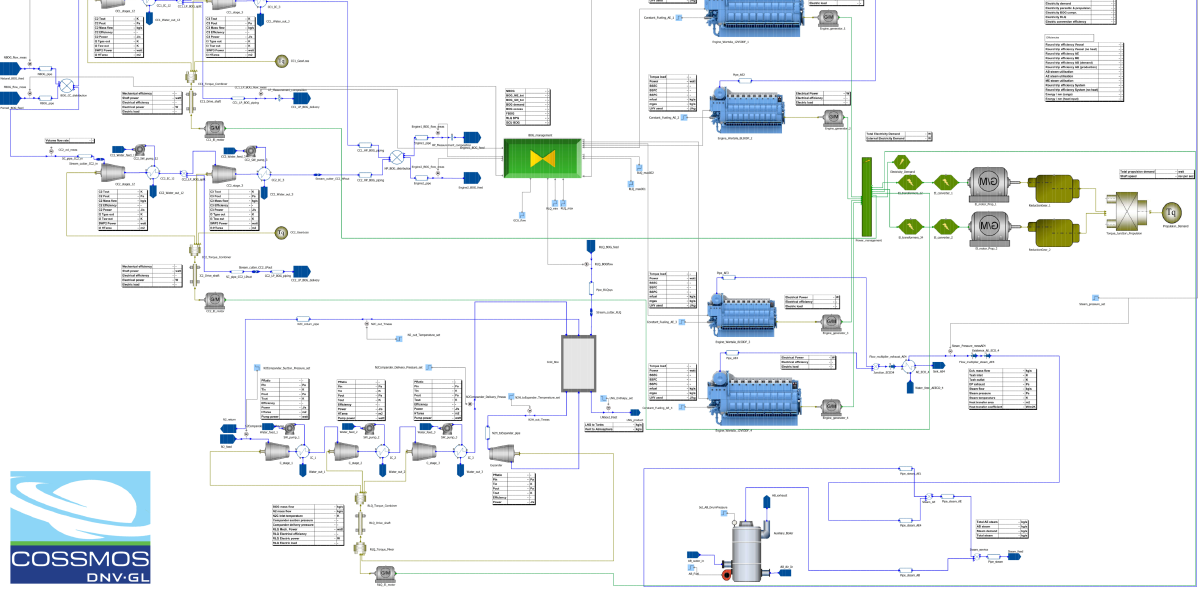
The total efficiency was assessed using an integrated systems approach. LNG carrier machinery systems are highly complex featuring tightly integrated sub-systems and components, like the BOG compression trains, gas management system, reliquefaction (if any), propulsion and/or generating engines, exhaust gas economisers and boilers. The primary fuel, i.e. boil-off gas, has variable properties depending on LNG cargo type and in-voyage boil-off rate conditions. In addition, the ships usually operate on a number of trading routes. Their operating profiles vary in terms of speed, propulsion, electrical and heat demand. The above features require a rigorous model-based approach, using DNV GL COSSMOS, to assess the integrated machinery system under realistic operating conditions as experienced by GasLog.
HHI and DNV GL carried out the hydrodynamic performance evaluation by comparing CFD simulations. Different CFD codes were applied for the comparison of resistance and self-propulsion performance but different scale effects were also considered. In addition, added resistance caused by wind and waves was investigated in order to ensure that the required power is sufficient for operation in the targeted environmental conditions.
Cargo containment optimisation was investigated by GTT and HHI. The tank shape, necessary reinforcements and boil off rate calculations, were examined to develop alternative cargo tank designs that could yield additional cargo capacity. With a starting design point of 174,000m3 cargo capacity, cargo tank optimisation by GTT and HHI allowed for a cargo capacity increase to 182,800m3, while maintaining the same main dimensions (length overall, breadth, draft) and taking into consideration newly introduced regulations and compatibility restrictions.
Nikolaos Kakalis, Manager of DNV GL Research & Development in Greece and responsible for COSSMOS development commented that “fusing unique competencies of key experts from across the industry, like HHI, GTT, and GasLog, with advanced tools like the COSSMOS machinery systems simulation and optimisation computer platform as well as state-of-the-art hull optimisation software, we bring innovation in practice that can generate tangible added value. As LNGreen utilizes existing technology it is important to stress that this concept design could be ordered today”.
Source: DNV GL Press Release
 IT
IT  en
en

